| TTN version: | TTNv3 / TTS SANDBOX |
| Frequency: | Europe 863-870 MHz (SF9 for RX2 – recommended) |
| Classes: | Ready for LoRaWAN Classes A, B and C |
| Using Docker: | Yes |
| Last updated: | July 20, 2025 |
This article provides instructions for making LoRa Basics Station using Raspberry Pi 3 or 4 and RAK5146 PiHAT Kit for LoRaWAN.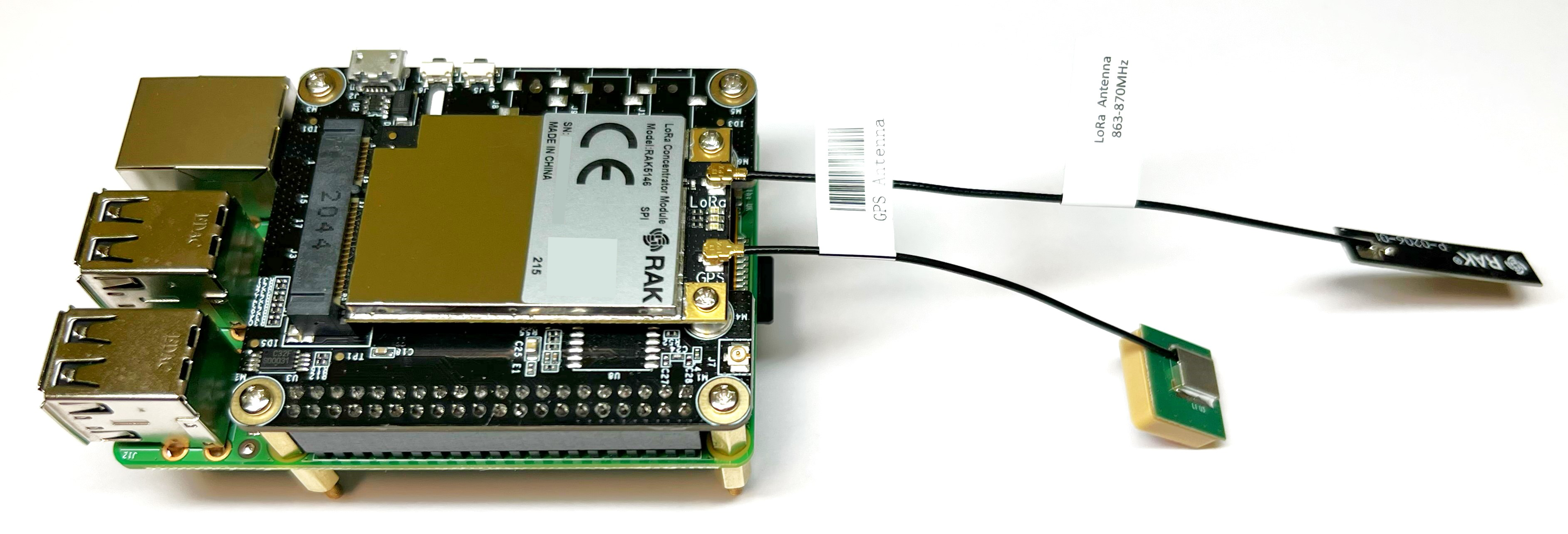
Note: The RAK5146 with GPS is required to support Class B end devices.
Prepare
- Raspberry Pi 3 or 4
- Raspberry Pi Power Supply
- microSD card
- RAK5146 PiHAT Kit for LoRaWAN (EU868, With GPS)
- PC
RAK5146 PiHAT Kit for LoRaWAN
The RAK5146 Kit consists of a RAK5146 SPI module powered by Semtech’s SX1303 baseband processor, a RAK5146/RAK2287 Pi HAT, and all the accessories you need. The Pi HAT is compatible with Raspberry Pi single-board computers (SBC) and others with the Pi 40-pin connector header.
RAK5146 Gateway Concentrator Module for LoRaWAN
The RAK5146 is an LPWAN Concentrator Module with mini-PCIe form factor based on Semtech SX1303. It can be used in any embedded platform offering a free mini-PCIe slot with SPI/USB connection. Furthermore, ZOE- M8Q GPS chip is integrated onboard for precise time synchronization.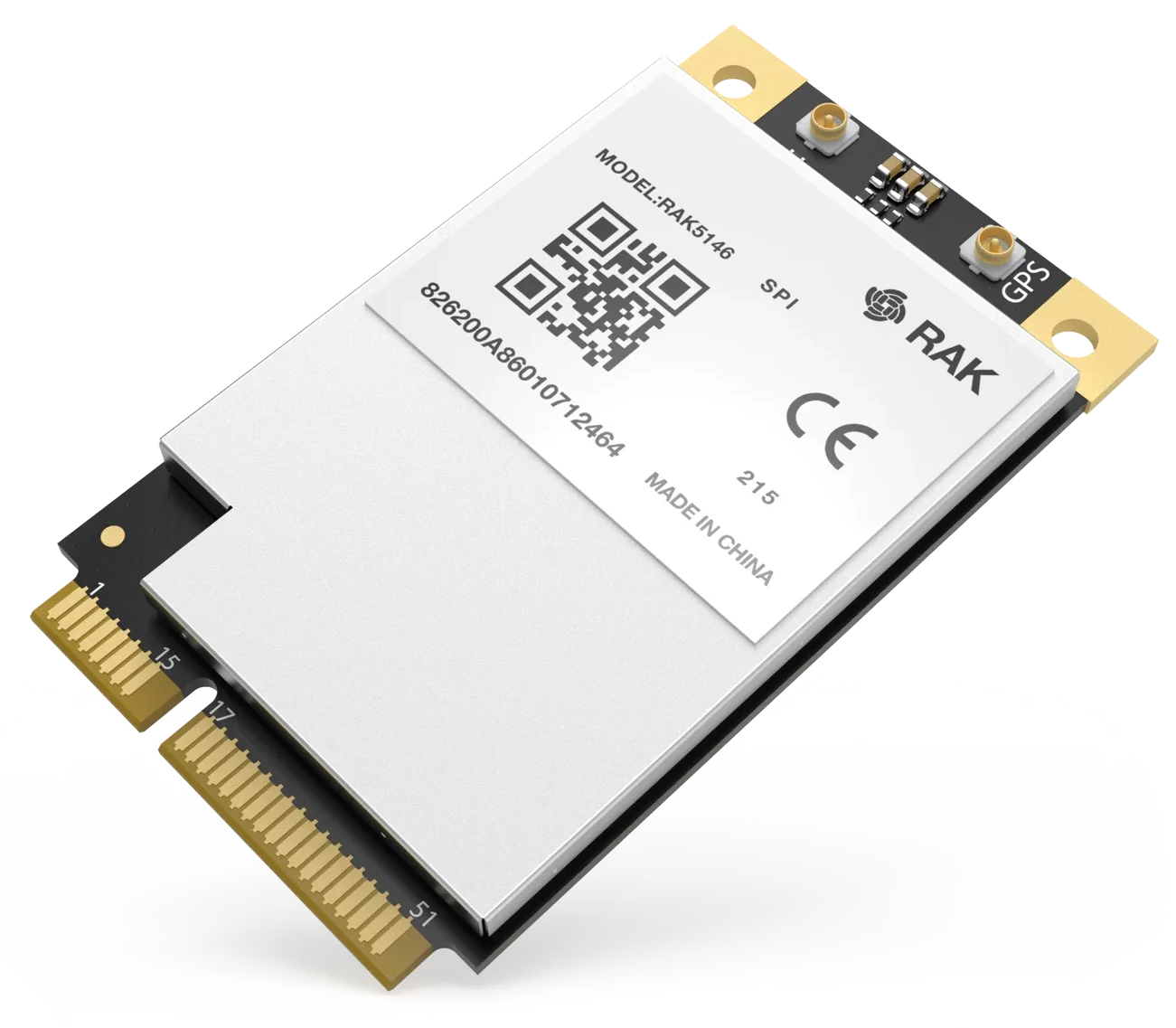
This module is an exceptional, complete, and cost-efficient gateway solution offering up to 10 programmable parallel demodulation paths, 8 x 8 channel LoRa packet detectors, 8 x SF5-SF12 LoRa demodulators, and 8 x SF5-SF10 LoRa demodulators. It is capable of detecting an uninterrupted combination of packets at 8 different spreading factors and 10 channels with continuous demodulation of up to 16 packets. This product is best for smart metering fixed networks and Internet-of-Things (IoT) applications.
For more information on RAK5146 Gateway Concentrator Module for LoRaWAN, see:
- RAK5146 Gateway Concentrator Module for LoRaWAN, SX1303 LoRa Core (SPI, GPS, non LBT)
- RAK5146 WisLink LPWAN Concentrator
- RAK5146 WisLink LPWAN Concentrator Datasheet
RAK2287/RAK5146 Pi HAT
RAK2287/RАК5146 Pi HAT is a converter board with a Raspberry Pi form factor that enables the RAK2287 SPI or RAK5146 SPI LPWAN concentrator modules to be mounted on the top of the Raspberry Pi. It integrates one 40-pin female Pi HAT connector and one mini PCIe connector.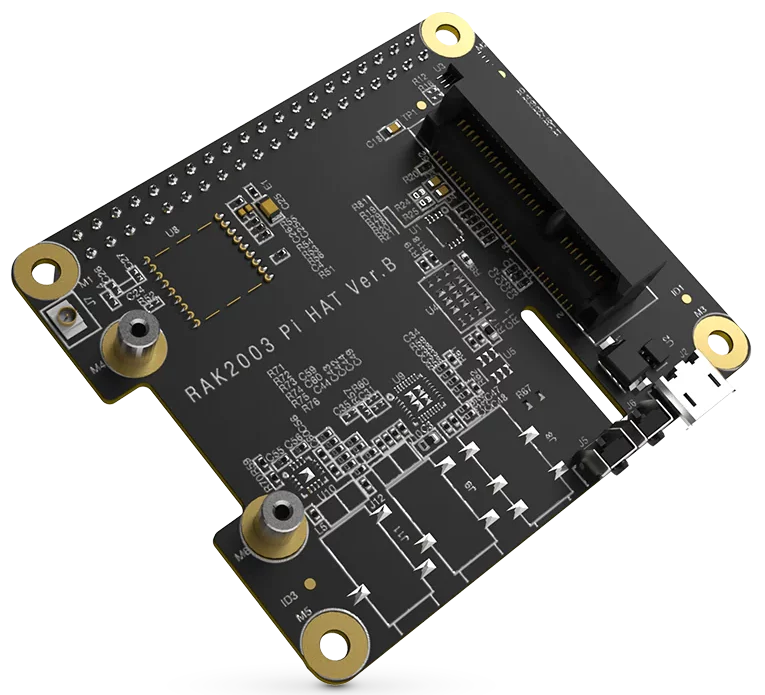
For more information on RAK2287/RAK5146 Pi HAT, see:
Assembly
- Prepare all the components.
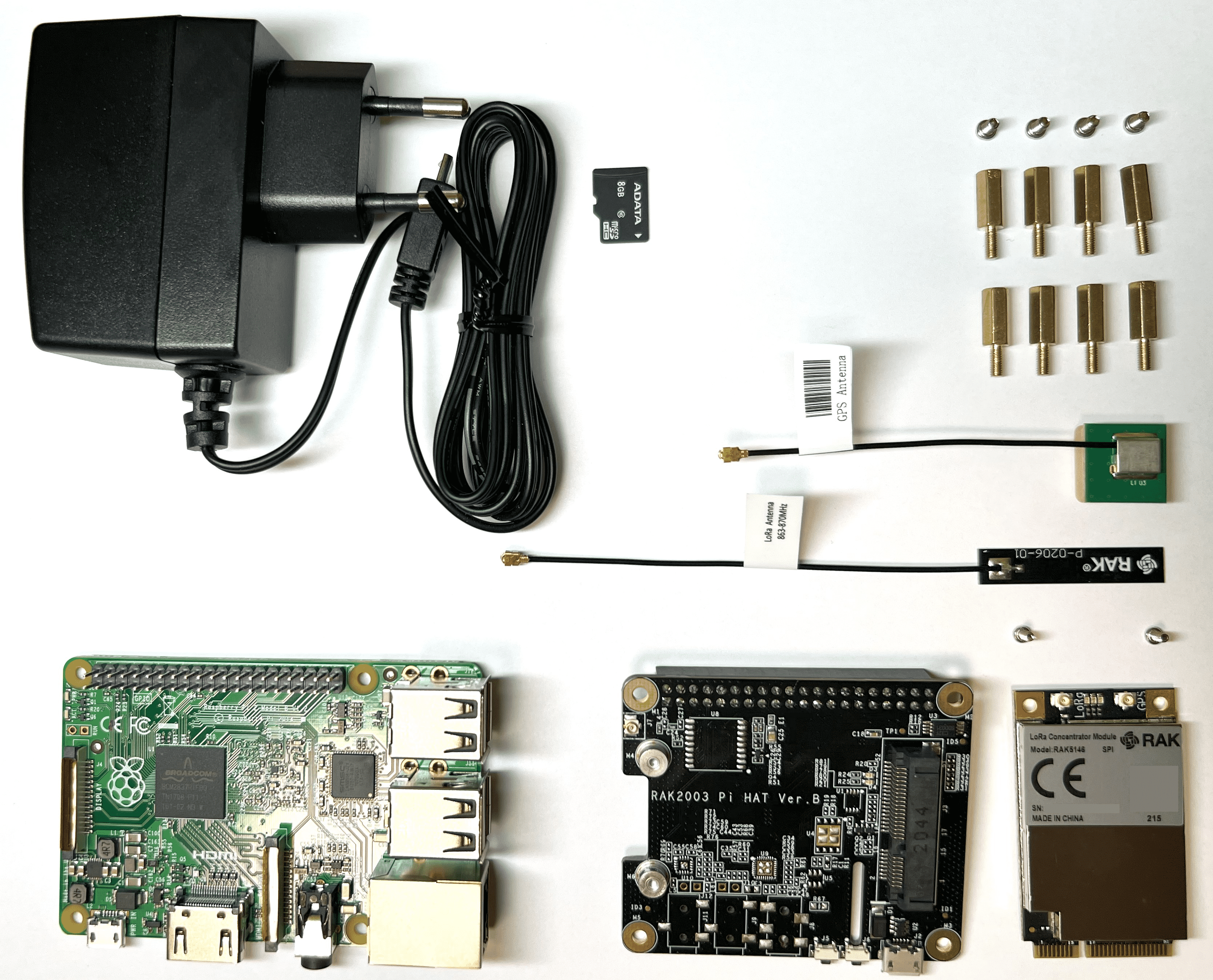
- Insert the LoRa Concentrator Module into the mini-PCIe slot on the RAK5146/RAK2287 Pi HAT and screw it in place with the two smaller screws from the package.
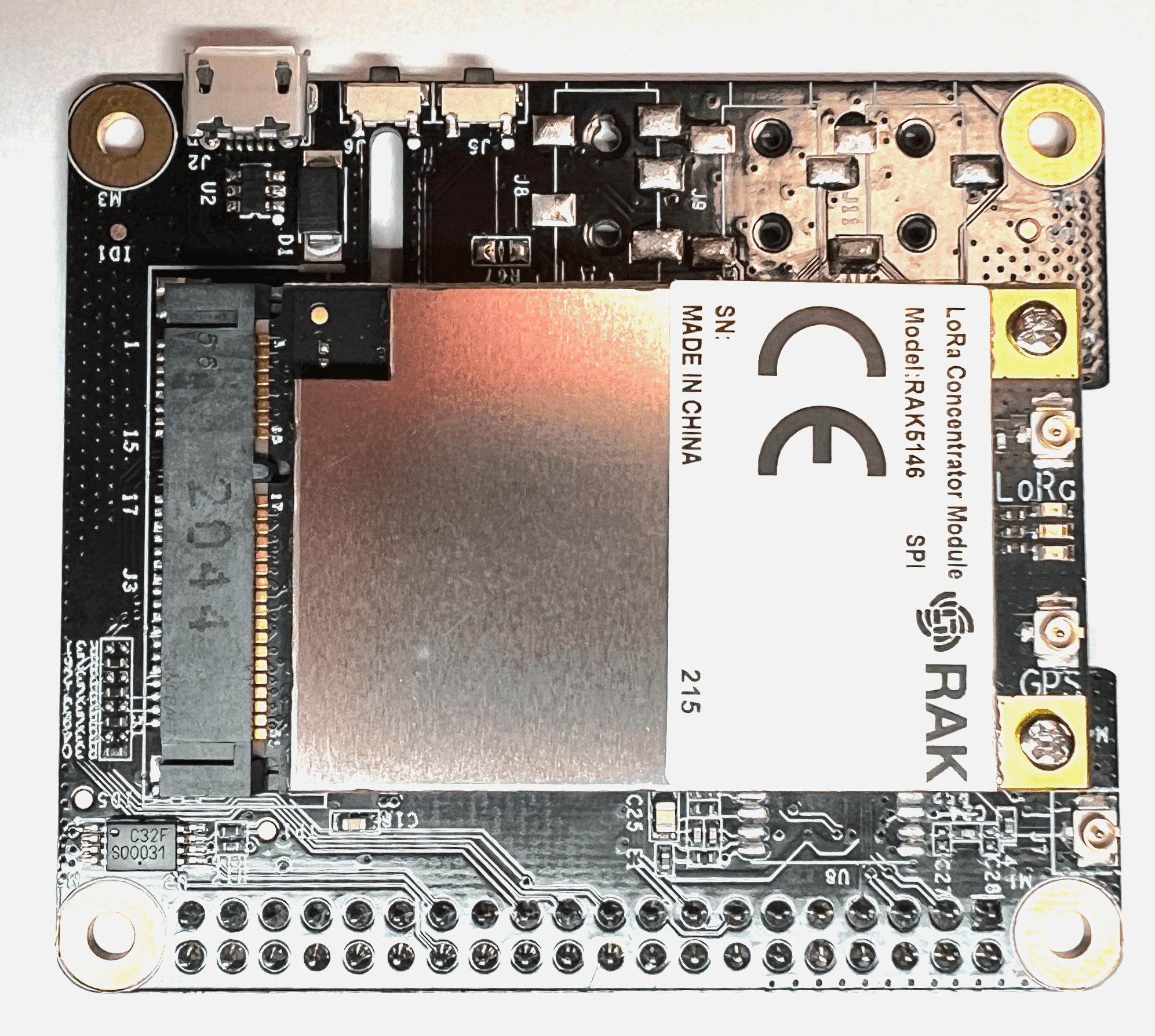
- Screw the spacers into the four mounting holes on the Raspberry Pi as shown in the following image.
- Connect the RAK5146/RAK2287 Pi HAT to the GPIO on the Raspberry Pi and screw it to the spacer posts with the four larger screws from the package.
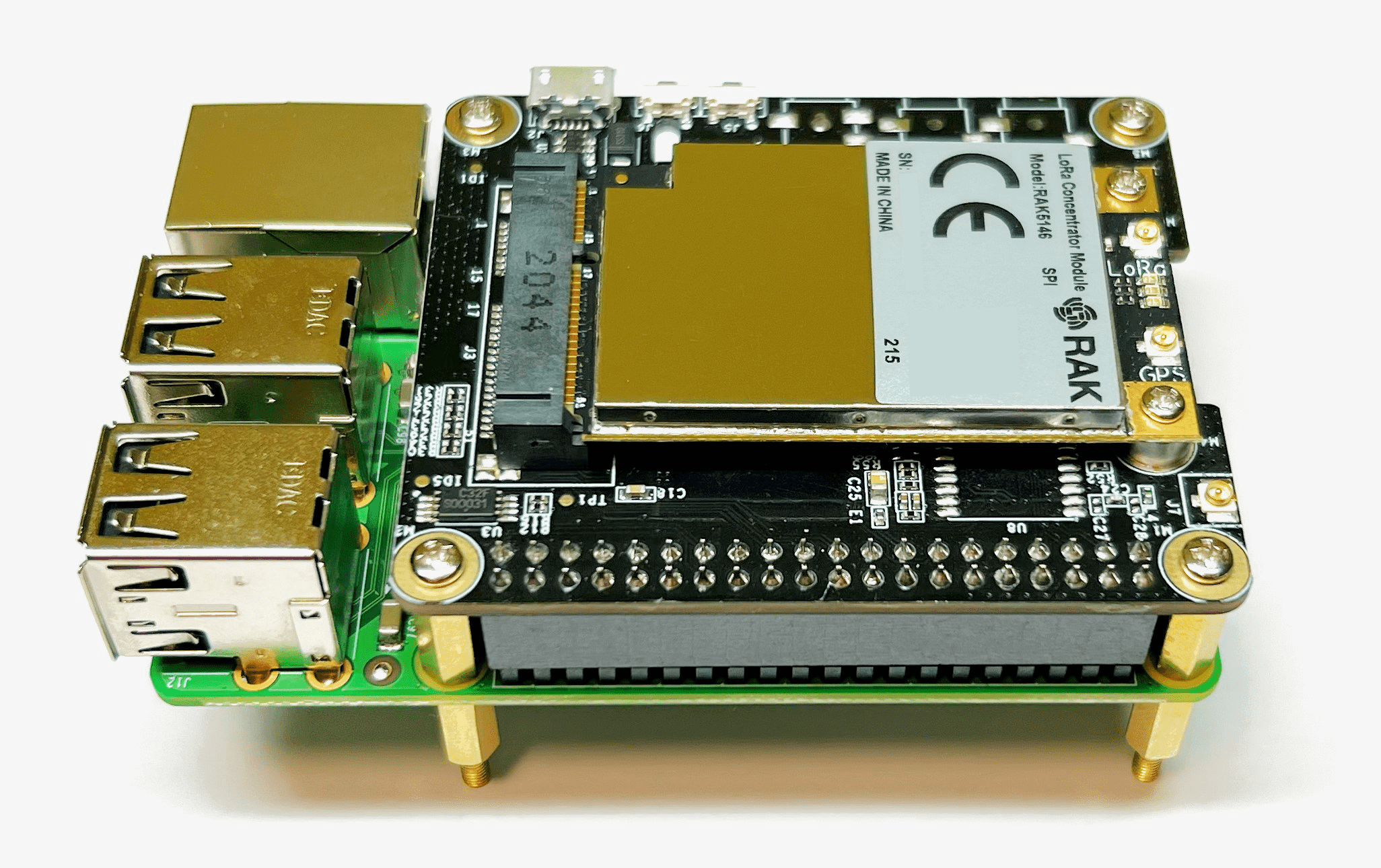
- Finally, connect the LoRa antenna and the GPS antenna to the LoRa Concentrator Module.

Raspberry Pi OS setup
- From https://www.raspberrypi.com/software/ download Raspberry Pi Imager and install it.
- Insert the microSD card into the computer.
- Run Raspberry Pi Imager.
- Click on CHOOSE OS.
- Click on Raspberry Pi OS (other).
- Click on Raspberry Pi OS Lite (32-bit).
- Click on CHOOSE STORAGE.
- Select the inserted microSD card on which you want to install Raspberry Pi OS.
- Click on Next.
- Would you like to apply OS customisation settings? – EDIT SETTINGS.
- Set hostname.
- Set username and password. (we recommend a 17-digit password containing lower and upper case letters, numbers and symbols)
- If you will use WiFi – Configure wireless LAN. (optional)
- Set locale settings.
- Click on tab SERVICES.
- If you will be connecting remotely via SSH – Enable SSH – Use password authentication. (optional)
- Click on SAVE.
- Click on YES.
- Click on YES.
- Click on CONTINUE.
- Insert the microSD card into the Raspberry Pi.
- Turn on the Raspberry Pi.
Remote connection via SSH (optional)
- Connect to your router and find the IP address of your Raspberry Pi.
- From a Windows PC, you can connect using Command Prompt (CMD) or PuTTY.
- On Windows PC open Command Prompt (CMD).
- Type
ssh -p port username@IP_Address(for example: ssh -p 22 loravsb@192.168.1.120). - Type your password.
Post-installation steps
- Update, upgrade and reboot Raspberry Pi. This will ensure that any security vulnerabilities are patched:
$ sudo apt update $ sudo apt full-upgrade $ sudo reboot
- Connect again via SSH.
- Use a different port for SSH and disable root login. First, open the SSH configuration file with a text editor:
$ sudo nano /etc/ssh/sshd_config
- Locate the line with
Port 22and change it to the desired port number (for example, change the port to 2222). Locate the line withPermitRootLoginand change its value tono(this will disable root login via SSH):Port 2222 PermitRootLogin no - Save the changes and exit the text editor.
- Restart the SSH service to apply the changes:
$ sudo systemctl restart ssh
- Log out and connect again via SSH on the new port.
- Install and configure the built-in firewall, ufw, to limit incoming network connections. In the
sudo ufw limit 2222/tcprule, change port 2222 to port you have chose for SSH above.$ sudo apt install ufw $ sudo ufw default deny incoming $ sudo ufw limit 2222/tcp $ sudo ufw enableNote: Firewall rules will have no effect on ports opened by Docker.
- Reboot Raspberry Pi:
$ sudo reboot
Docker
- Connect again via SSH.
- Install the latest Docker version using the convenience script provided by docker:
$ curl -fsSL https://get.docker.com -o get-docker.sh $ sudo sh get-docker.sh $ sudo groupadd docker $ sudo usermod -aG docker $USER $ newgrp docker $ sudo systemctl enable docker.service $ sudo systemctl enable containerd.service
For more information on Docker installation, see https://docs.docker.com/engine/install/.
LoRa Basics Station setup
- First, get the Gateway EUI by running the following command:
$ cat /sys/class/net/eth0/address | awk -F\: '{print toupper($1$2$3"FFFE"$4$5$6)}'
The Things Stack
- Create an account on The Things Network if you don’t have one.
- Login on The Things Network.
- Click on your username and choose Console.
- Select a network cluster.
- Go to gateways.
- Click on button + Register gateway.

- Write the previously detected Gateway EUI in the Gateway EUI field.
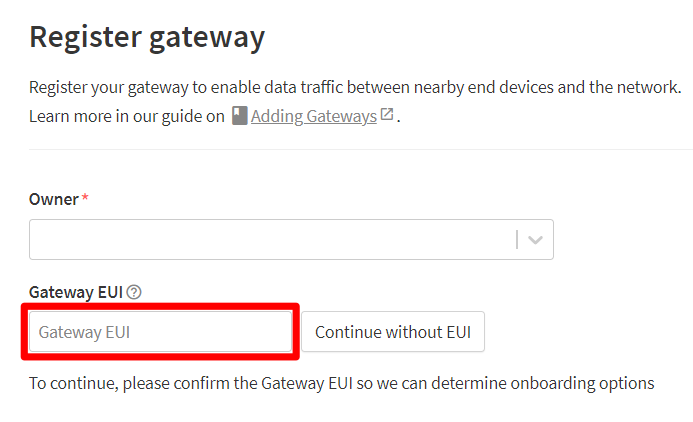
- Click on button Confirm.
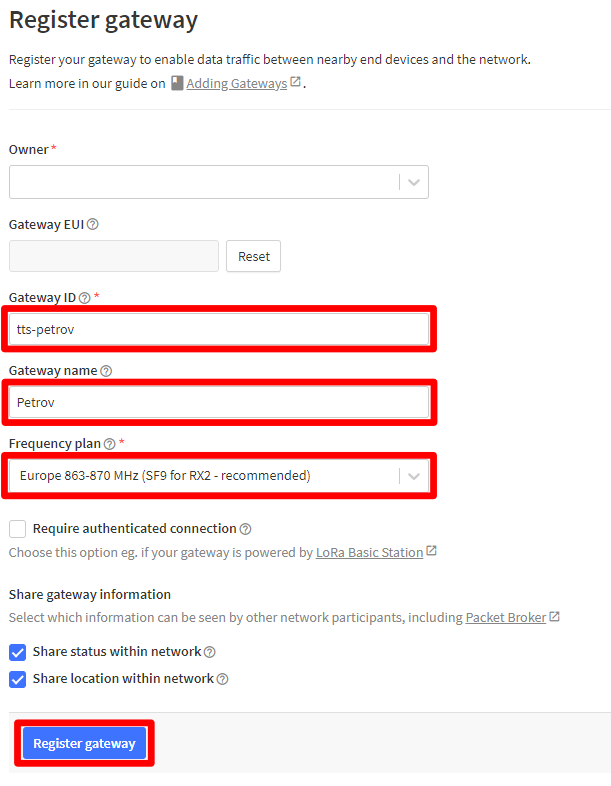
- Write something into Gateway ID.
- Write something into Gateway name.
- Frequency plan – Europe 863-870 MHz (SF9 for RX2 – recommended)
- Click on button Register gateway.
- In API keys click on button +Add API key.
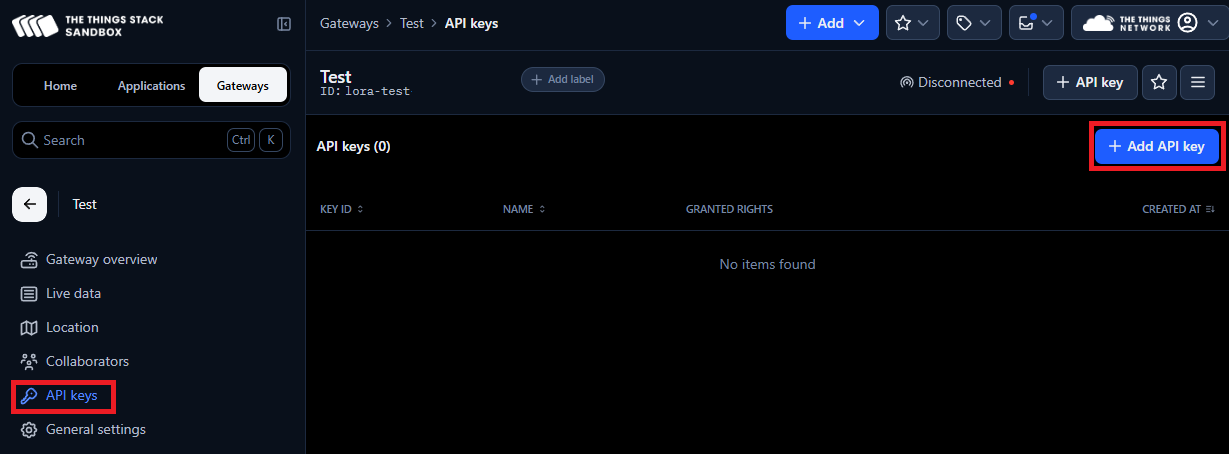
- Write something into Name.
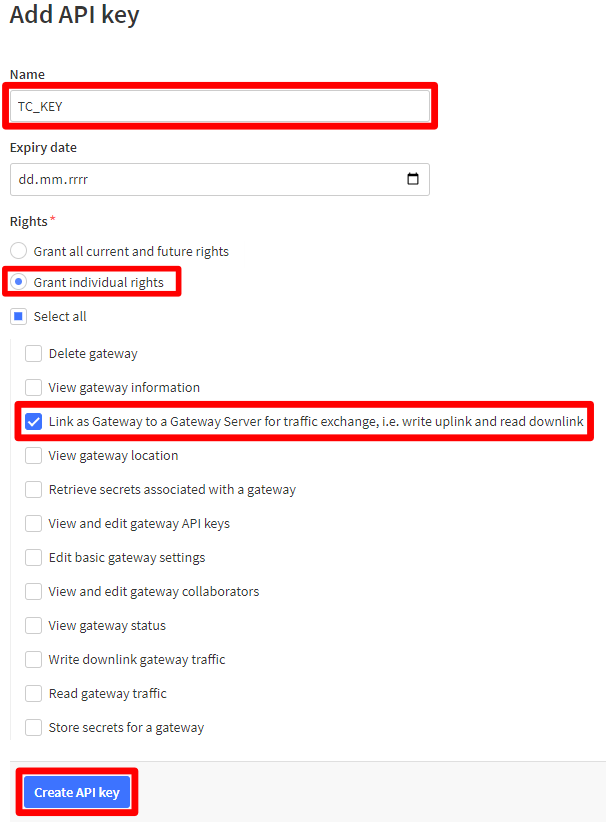
- Click on Grant individual rights.
- Select Link as Gateway to a Gateway Server for traffic exchange, i.e. write uplink and read downlink.
- Click on button Create API key.
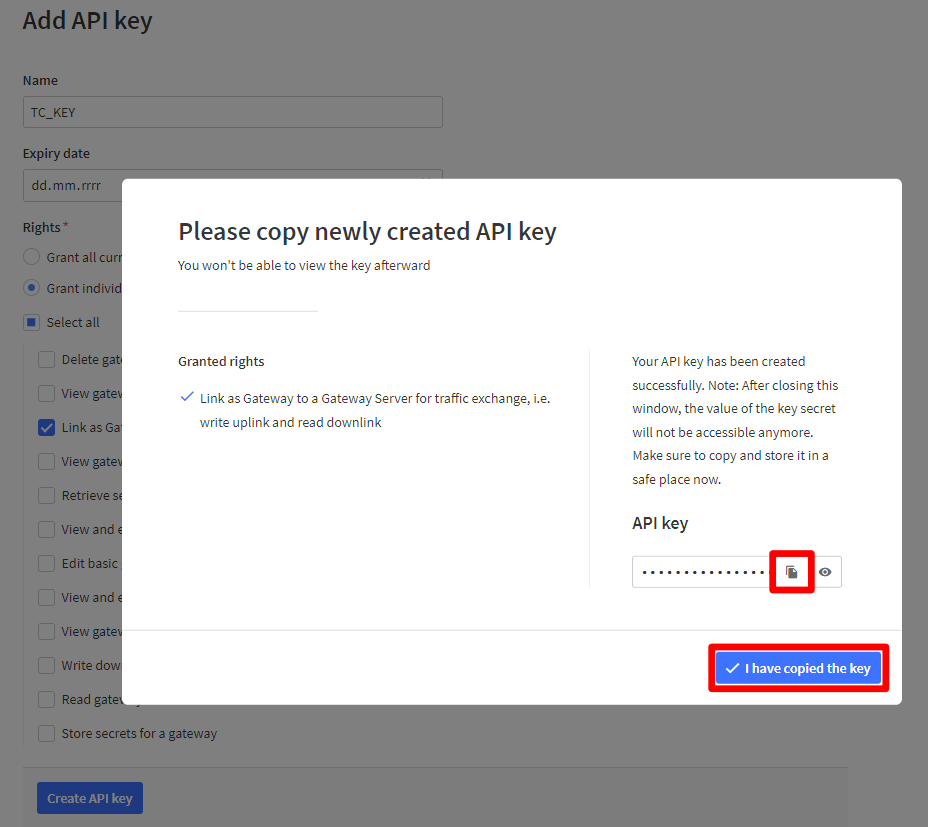
- Click the Copy to clipboard button and paste the key into some text document for future use.
- Click on button I have copied the key.
Raspberry Pi’s Interfaces
- Run the following command to configure the Raspberry Pi’s Interfaces:
$ sudo raspi-config
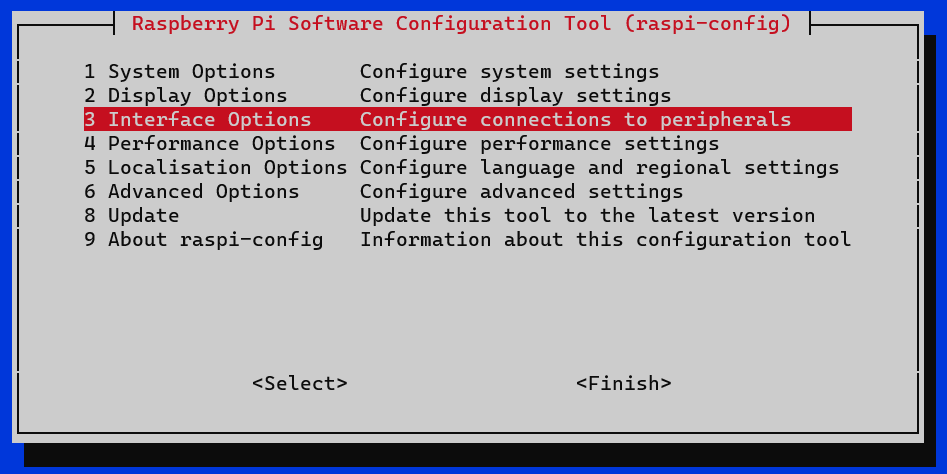
- In 3 Interface Options -> I4 SPI.
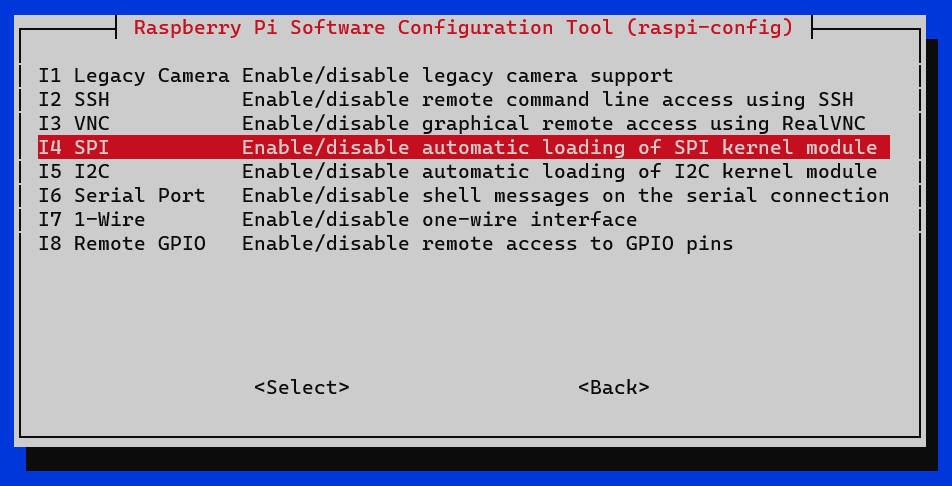
- Would you like the SPI interface to be enabled? -> Yes.
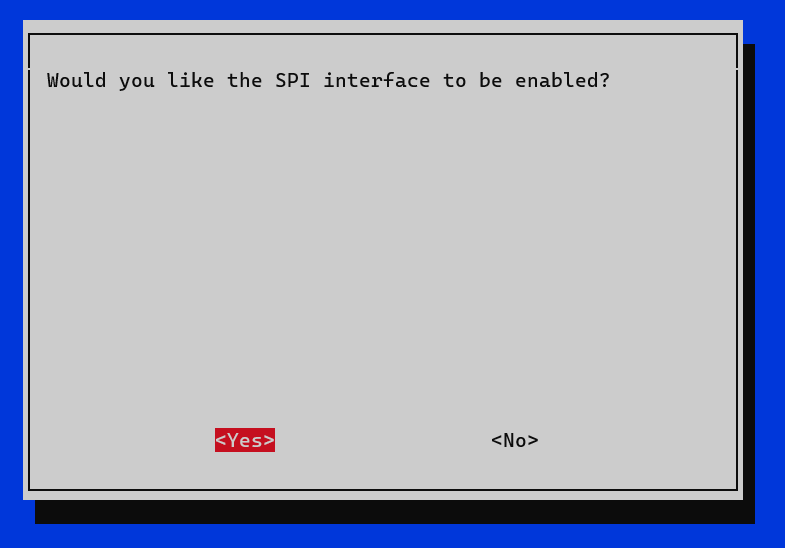
- Ok.
- In 3 Interface Options -> I5 I2C.
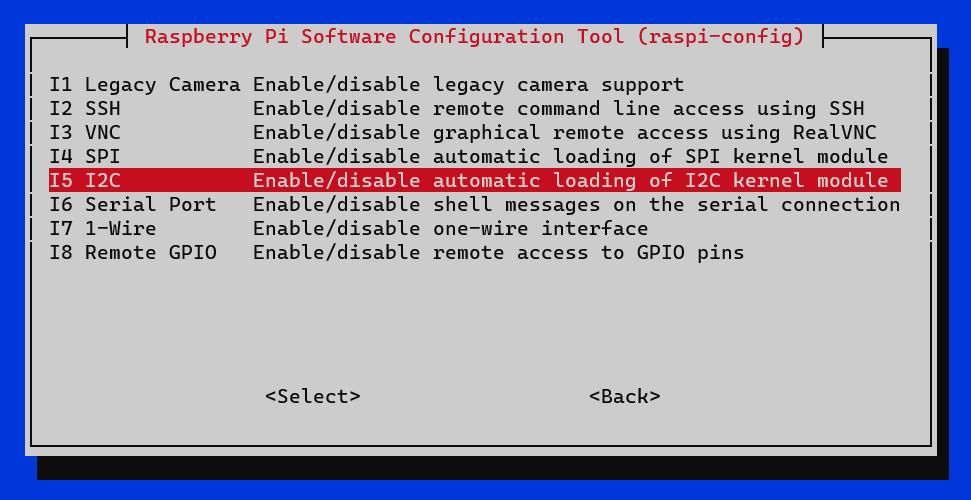
- Would you like the ARM I2C interface to be enabled? -> Yes.
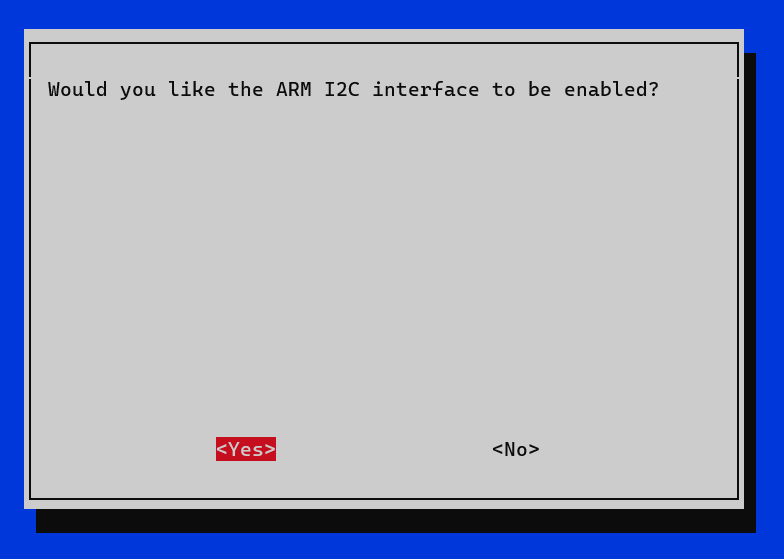
- Ok.
- In 3 Interface Options -> I6 Serial Port.
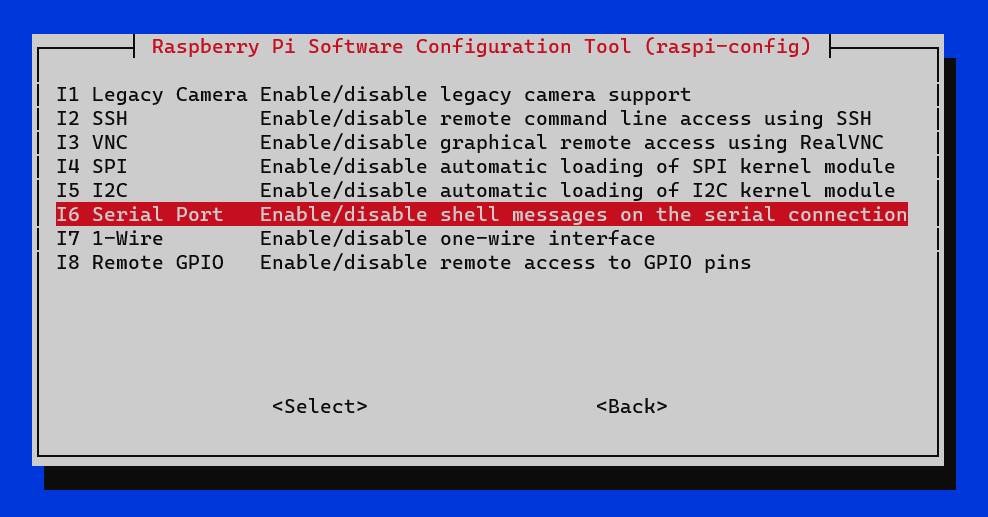
- Would you like a login shell to be accessible over serial? -> No.
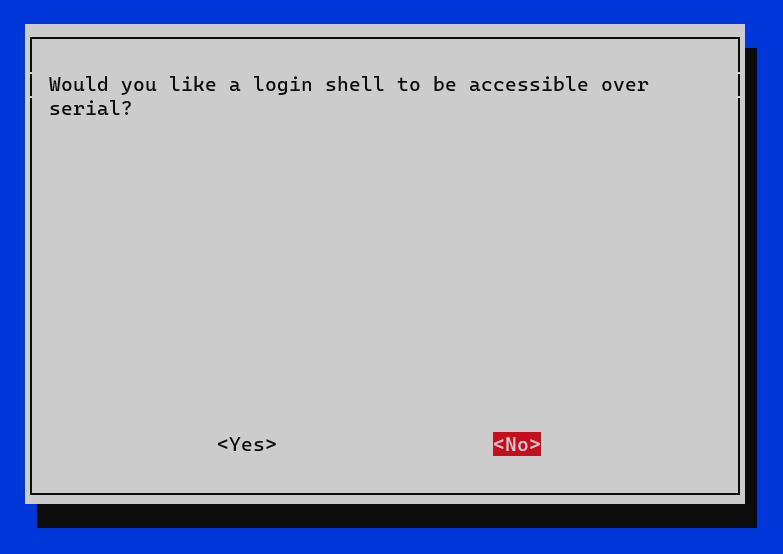
- Would you like the serial port hardware to be enabled? -> Yes.
- Ok.
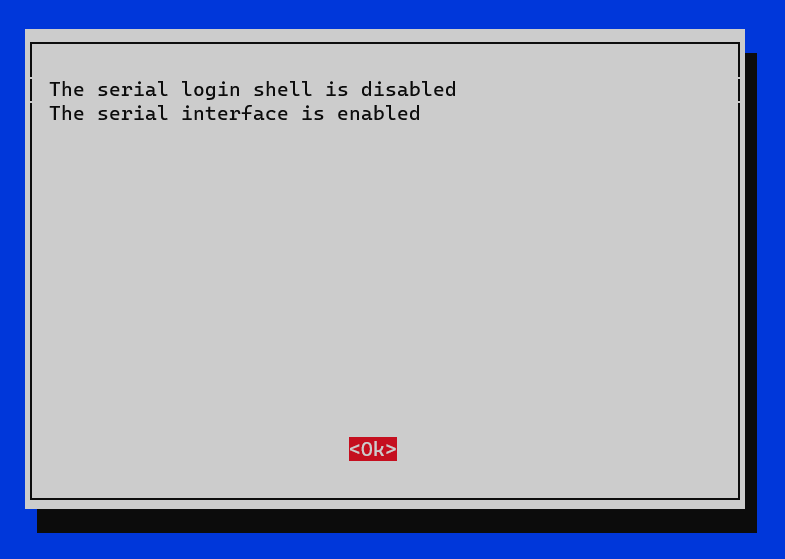
- Finish.
- Would you like to reboot now? -> Yes.
LoRa Basics Station
- Connect again via SSH.
- Run this command to create and edit the docker-compose.yml file:
$ sudo nano docker-compose.yml
- Copy and paste the configuration below into your docker-compose.yml file. Copy and paste the API key you got previously saved to the TC_KEY variable.
version: '2.0' services: basicstation: image: xoseperez/basicstation:latest container_name: basicstation restart: unless-stopped privileged: true network_mode: host # Required to read main interface MAC instead of virtual one environment: MODEL: "RAK5146" TC_KEY: "NNSXS...." # Copy here your API key from the TTS USE_LIBGPIOD: 1 - Run this command to pull the image from the Docker Hub:
$ sudo docker compose pull
- Now, you can start it running in the background with the following command:
$ sudo docker compose up -d
- Finaly, check that the gateway status is Connected in the TTS console.
For more information on LoRa Basics™ Station for Docker, see:
